Ford F250 A/C compressor NOT working (10 reasons WHY)
Hot air coming out of your Ford F250's ac system is terrible on a hot day.
A common cause for this is because the A/C compressor is not turning on.
Modern cars need proper diagnostics when finding problems with the air conditioning system.
This article will help you pinpoint the issue with your compressor so you can have cold air back in your Ford F-250 Super Duty!
Here are 10 common reasons why the A/C compressor won't turn on.
Refrigerant level
Electrical problems
AC compressor clutch
Evaporator temperature sensor
Pressure sensor
Engine faults
Bad A/C button or control module/head unit
A/C Compressor clutch relay
Bad A/C compressor
Broken drive belt
Refrigerant levels
The most common reason why an A/C compressor is not turning on is because of a freon leak. A refrigerant leak can be anywhere in the A/C system but can be easily found with the proper tools.
Small leaks can be a headache for most mechanics, but using dye in the A/C system can help identify the leak.
It is not recommended to use the DIY kits of freon or a recharging kit. Most kits come with a sealant that is supposed to repair leaks in the A/C system. In most cases, they do not work and only clog important components like the evaporator core and orifice tube.
It is possible to over charge your A/C system. This will cause the A/C compressor to not come on, also.
Solution:
When you start to feel cool air and not cold air, it is important to have a professional mechanic use the proper A/C machine to fill the system in your car to the proper level.
Electrical Issues
Electrical issues can plague a car owner. Whether it is a broken wire, blown fuse, or poor ground, all of these can cause the A/C compressor to not turn on.
An A/C compressor has to have a proper power supply and a good ground to work correctly. A tool to check this is a digital voltmeter, a test light, or a Power Probe.
Solution:
Check the wires going to the A/C compressor. There should be power and ground. If there is only one wire, then it is generally the power and the whole compressor is grounded to the engine block.
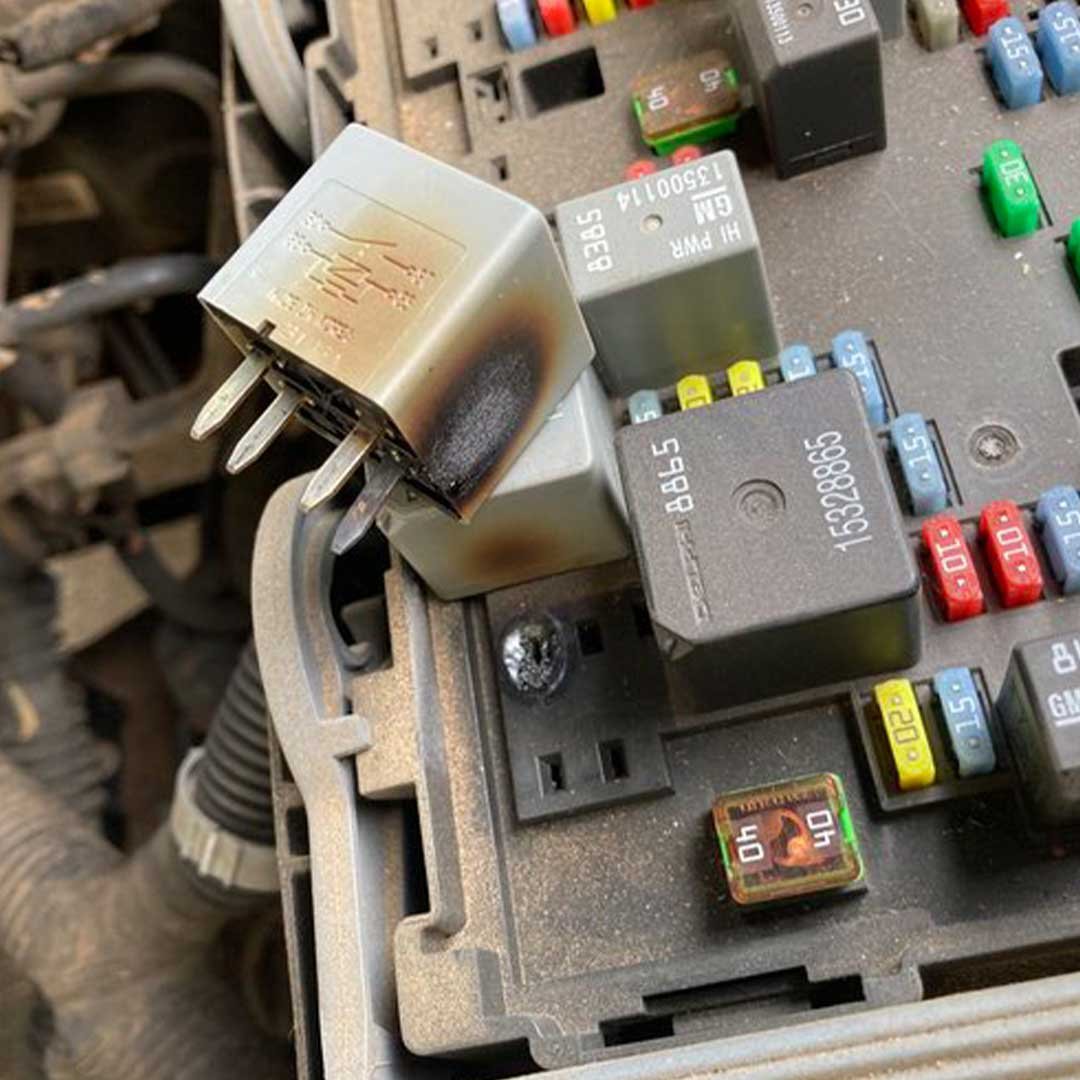
If there is no power, then there is a blown fuse, bad relay, or an open circuit caused by a broken wire.
The fuse box is a great place to start looking for electrical issues.
Check out this case study about a Jeep with A/C problems from a wiring issue.
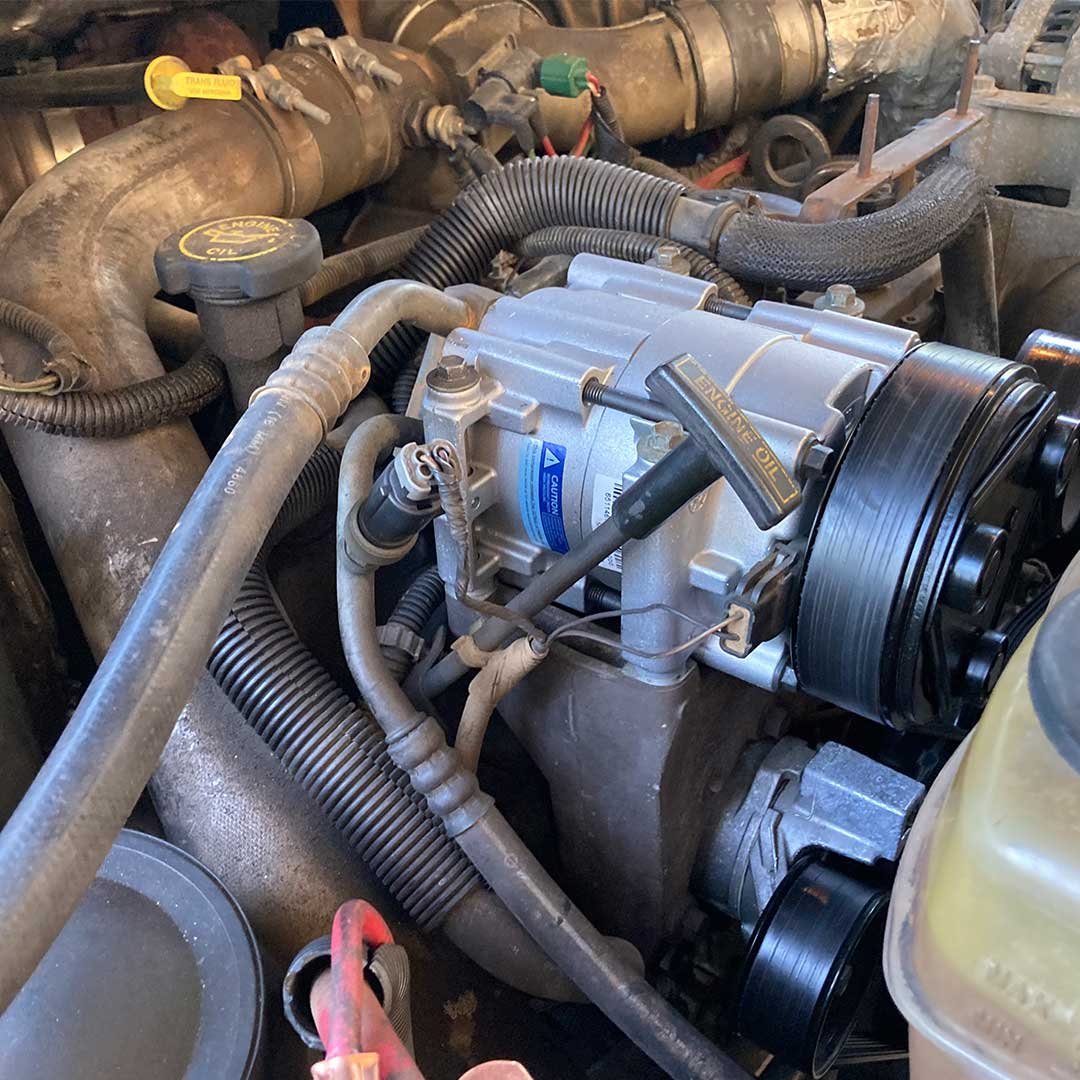
A/C Compressor Clutch
The A/C compressor's clutch is the mechanical portion on front of the A/C compressor that uses the rotation of the drive belt to rotate the compressor shaft. When the clutch is off, the internal portion of the A/C compressor is not turning. When the clutch is on, the internal portion of the A/C compressor is turning.
Solution:
I would replace the whole A/C compressor, but there are kits that allow you to replace just the ac clutch.
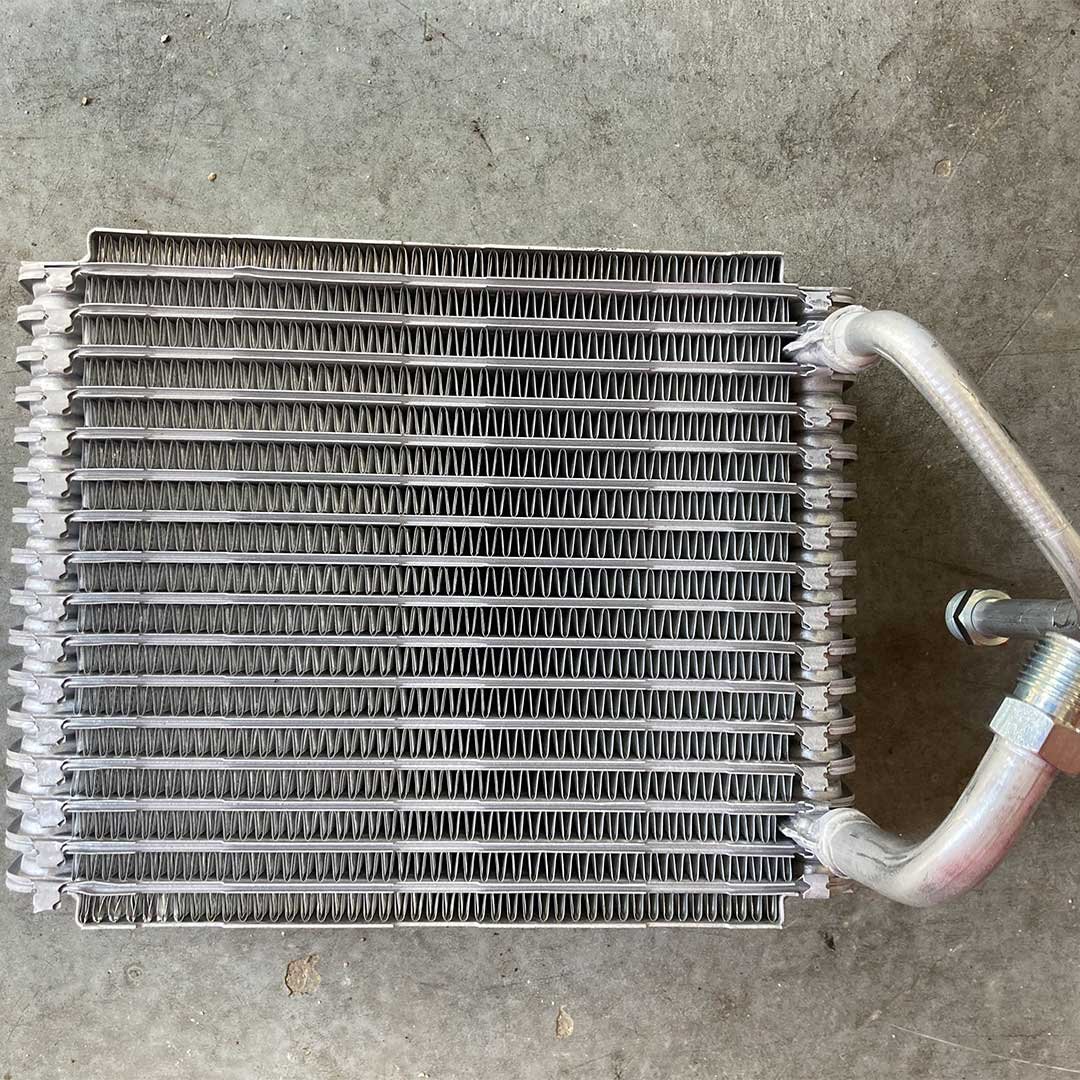
Evaporator Core Temperature Sensor
Evaporator Core Temperature Sensor
The evaporator core temperature sensor is a small sensor that is located in the vanes of the evaporator core. This sensor monitors the temperature of the evaporator core to ensure that the correct temperature is in the cabin and so the evaporator core does not freeze over.
If the evaporator core temperature sensor's voltage is incorrect, it can tell the engine's computer to turn the A/C compressor off.
This sensor can trick a lot of DIY-mechanics if they do not know of it.
An advanced scan tool will be needed to monitor the evaporator core temperature sensor to make sure it is reading the correct temperature.
Check out this case study of a Chevrolet Suburban where this happened.
Solution:
Replace the evaporator temperature sensor. This usually requires removing the dashboard to access the HVAC housing.
Evaporator Core
Pressure Sensor Issues
The A/C system uses pressure switches to turn the A/C compressor on and off. If the pressure of the freon is too high or too low, the A/C compressor will turn off. Incorrect pressures can be caused by too much or too little freon, clogs, or faulty components.
The A/C system generally uses a low-pressure switch and a high-pressure switch. If a pressure switch is not indicating the correct pressure, then the A/C system will not work properly.
Solution:
Replace the low or high-pressure sensor if needed.
Engine Fault
Trouble with the engine including certain fault codes or misfires can cause the A/C compressor to not turn on.
The engine control module monitors the engine for certain issues. Issues that take away power or cause low battery voltage, can make the engine control module keep the A/C compressor from turning on.
Solution:
Repair any engine trouble codes that can cause the engine control module to turn the A/C compressor off.
Check out this article about how the engine code P0128 disabled the A/C compressor along with other components on a Chevy Colorado.
Bad A/C button or Climate Control Module
The button (or AC switch) on your dash that turns the A/C compressor "on" is usually a part of the A/C system control module (sometimes called a head unit). When the button on the dash is pressed to the "on" position, it sends a signal to the engine control module to turn the A/C compressor on.
If the button does not work or the control module is not sending a signal out, then the A/C compressor will not turn on.
Solution:
Replace the A/C control module or button. In some cases, it has to be programmed.
A/C Compressor Clutch Relay
The A/C compressor clutch relay is part of the circuit that gives the A/C compressor clutch voltage to turn on. The engine control module turns the relay on and the relay sends power from a fuse to the A/C compressor clutch. Over time, a relay can become bad and not work properly.
Solution:
Replace the A/C compressor clutch relay.
Check out this case study of a bad relay not allowing the radiator fans to come on!
Not sure where the A/C compressor clutch relay is located on your car? Try AlldataDIY!
Bad A/C Compressor
An A/C compressor problem is sometimes just the AC compressor itself. The A/C compressor can become internally damaged and not work, even though the clutch is engaged.
Low compressor oil levels and old age can cause A/C compressor failure.
Solution:
Install a new compressor.
Broken Drive Belt
The drive belt (or serpentine belt) is what drives the pulley on the A/C compressor. When this breaks, you will lose the operation of the A/C compressor.
Some vehicles have one large drive belt, but others can have separate belts that drive different systems. For example, newer GM vehicles can have a drive belt for the A/C compressor alone while all other accessories are driven by another belt.
Solution:
Replace any broken or cracked drive belt.
Other parts of an A/C system that go bad
A/C Condenser
The A/C condenser (sometimes called condenser coil) is on the front of the vehicle, right before the radiator. It can become clogged with debris from the road.
Expansion Valve
The expansion valve changes the state of the refrigerant from a liquid to a gas.
Radiator Fans
The radiator fans are essential to the A/C system. They move air through the A/C condenser to cool the freon inside. If they are not working properly it will cause the A/C system to not function properly.
Orifice Tube System
An orifice tube is a crucial part of the A/C system. It controls the flow of refrigerant through the evaporator core by allowing the refrigerant to expand. The orifice tube has a mesh screen and can become clogged.
Charging an A/C system
When charging an A/C system in a car, it is important to use the correct equipment. An A/C machine is needed to properly recover, vacuum, and charge the system.
Using the high side and low side pressure port, the A/C machine can charge the system with enough refrigerant to function as it should.
Here is an article about low airflow through the vents.
In the article, you'll see that it can be any of these issues.
Blower motor
Blower motor resistor
Clogged evaporator coil
Cabin air filter
The first thing you should do when suspecting a faulty compressor is to have a professional inspect it. It could be a simple fix to repair your car's air.
Disclaimer and Disclosure:
Due to factors beyond the control of DiagnosticMechanic.com, it cannot guarantee against unauthorized modifications of this information, or improper use of this information. DiagnosticMechanic.com assumes no liability for property damage or injury incurred as a result of any of the information contained in this website. DiagnosticMechanic.com recommends safe practices when working with power tools, automotive lifts, lifting tools, jack stands, electrical equipment, blunt instruments, chemicals, lubricants, or any other tools or equipment seen or implied in this website. Due to factors beyond the control of DiagnosticMechanic.com, no information contained in this website shall create any express or implied warranty or guarantee of any particular result. Any injury, damage or loss that may result from improper use of these tools, equipment, or the information contained in this website is the sole responsibility of the user and not DiagnosticMechanic.com.
DiagnosticMechanic.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. In many of our case studies, articles, and tool reviews, we may earn a small commission when readers purchase products through our links.