Do you have to replace brake pads and discs at the same time?
Brake rotor that is too thin on one side
Performing regular maintenance on your brake system requires a multitude of things to do and remember. New parts, tools, and the knowledge to take things apart and put them back together correctly are a big part of what it takes to replace brakes.
When installing new brake pads, it's a good idea to evaluate all of the maintenance options that could prevent a future brake problem.
There is one question that some people still ask when it comes to brake pad replacement or brake repair.
Do you have to replace brake pads and discs at the same time?
When there is excessive shaking from the brake discs (brake rotors) or the minimum thickness of the brake discs has been met, then yes, they will need to be replaced along with the brake pads.
Metal-on-metal sound from low brake pads contacting the brake rotor surface.
Here are some questions to help you decide if your brake rotors need to be replaced.
Does your steering wheel shake when applying the brakes?
Front brakes that have warped rotors can generally be felt in the steering wheel. This is because the steering components that are connected to the front wheels are shaking because of the warped rotor.
Does your brake pedal pulse when applying the brakes?
In some cases, warped rotors in the rear brakes can be felt through the brake pedal.
Is your brake rotor too thin?
Using a special tool called the micrometer, you can measure the thickness of the brake rotor. A general rule is 1/4 inch. Anything below this needs to be replaced. Of course, check what your owner's manual says about rotor thickness. Some manufacturers want you to replace the rotor for every brake job.
Does your vehicle manufacturer have a specific time or mileage they want you to replace your old rotors?
car manufacturers list out in the owner's manual the proper maintenance intervals for your specific vehicle.
Do your brake rotors look too scarred or have deep grooves on the surface?
A visual inspection of your brake rotors may reveal excessive scarring. Deep cuts on the side of the rotor are not good. Brake pads can not make good contact with the deep cuts, which can result in poor braking. A smooth surface is what is needed for good braking performance.
This caliper piston was pushed too far out because of low brake pads. The low brake pads also put deep grooves in the brake rotor surface.
What are some other things that cause the car to shake when braking?
Brake caliper
The caliper piston may be causing uneven wear to the brake pads. You may notice one brake pad is worn more than the other. This could mean the caliper piston is becoming stuck. A stuck caliper piston can cause excessive heat on the brake rotor.
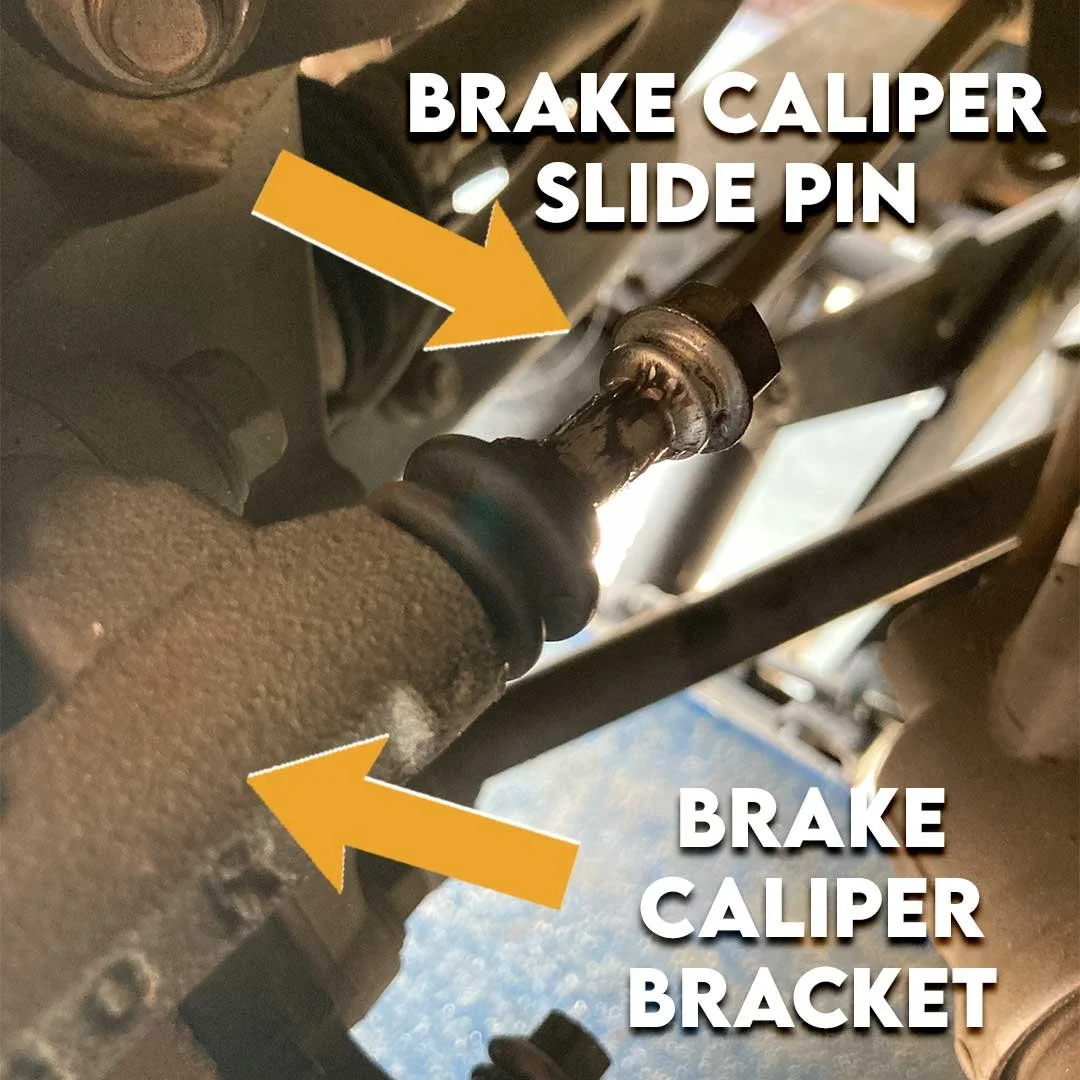
Slide pins
A sticking slide pin may also cause uneven brake pad wear, which can result in excessive heat on the brake rotor.
Front brake pads and rear brake pads
How to measure rotor thickness?
Measuring brake rotor thickness can help you determine whether your brake rotors should be replaced.
Find the minimum thickness for your brake rotors. This may be in your owner's manual. In some cases, it can be found on the brake rotor. If not, try Alldata DIY for your car's specifications.
Place a micrometer at the thinnest point of the brake rotor. Be sure to place the micrometer in the areas where the brake pads contact the brake rotor.
Measure multiple areas to ensure you have measured the thinnest area.
If the measurement is thinner than the minimum thickness, then the brake rotors need to be replaced.
When changing brake pads and rotors, make sure the slide pin moves freely.
What causes brake rotors to wear out?
Here are three major causes of brake rotors wearing out:
Hard or Sudden Stops - Emergency stops cause excessive heat to build up quickly on the brake rotors. This can cause brake rotor warping.
Long Braking Periods - Excessive heat from riding the brake can cause brake rotor wear. Brake rotors need time to cool down in between excessive braking.
Worn Brake Pads - Low brake pads can cause scarring on the surface of the brake rotor. When a brake pad has gotten too low, it can cause metal-on-metal contact with the brake rotor. This contact can cause deep grooves in the surface of the brake rotor.
Can I have my brake rotors machined or "turned" instead of replacing them?
Yes, as long as they are not below the minimum thickness. Note that when a brake rotor is "turned,” it makes the brake rotor easier to heat up and warp again. Excessive heat from hard braking can cause a thin brake rotor to warp quickly.
Driving style has a huge influence on how quickly brake rotors are warped. Slow, easy stops can reduce the amount of heat that the brake rotors take. A hard stop causes excessive heat build-up on the brake rotors.
Machining or "turning" a brake rotor means smoothing out the warped areas of the rotor surface. A car brake lathe is used in this process and it cuts away the uneven areas, or high points(spots), that can cause shaking when the brakes are applied.
What do I need to perform a complete brake service?
New rotors
New brake pads
Brake lubricant
Brake fluid
Car jack and jack stands
Socket set
For caliper, caliper bracket, etc.
Lug nut wrench or Impact with impact sockets,
Be sure not to strip the lug nuts when removing them.
Torque wrench
To torque bolts to proper specification.
Brake piston tool and brake caliper hanger
Flat surface and wheel chocks
Your car may need specialty tools. Following a quick Youtube video or blog on your specific vehicle can factor in the need for specialty tools.
Don't have these tools? There is good news! Ask your local auto parts store if they have a tool rental program. They may be able to provide you with the exact tool you need.
Brake rotor that is beyond repair. This brake rotor damaged the brake caliper.
Routine maintenance of your vehicle may mean that brake rotors need to be replaced. Watch for warning signs like brake noise or shaking to help prevent any bad accidents from brake failure.
Have a professional mechanic perform a brake inspection when you schedule oil changes. A professional option after a test drive can be useful information when making the decision.
Whether it's installing new pads, a master cylinder, or other brake components, make sure to perform the job correctly.
Use Alldata DIY to find the correct repair procedures and torque specifications for your vehicle.
Alldata DIY is a leading source of online automotive diagnostic and repair information.
For more information about when to replace brake pads and rotors, click the button below!
Disclaimer and Disclosure:
Due to factors beyond the control of DiagnosticMechanic.com, it cannot guarantee against unauthorized modifications of this information, or improper use of this information. DiagnosticMechanic.com assumes no liability for property damage or injury incurred as a result of any of the information contained in this website. DiagnosticMechanic.com recommends safe practices when working with power tools, automotive lifts, lifting tools, jack stands, electrical equipment, blunt instruments, chemicals, lubricants, or any other tools or equipment seen or implied in this website. Due to factors beyond the control of DiagnosticMechanic.com, no information contained in this website shall create any express or implied warranty or guarantee of any particular result. Any injury, damage or loss that may result from improper use of these tools, equipment, or the information contained in this website is the sole responsibility of the user and not DiagnosticMechanic.com.
DiagnosticMechanic.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. In many of our case studies, articles, and tool reviews, we may earn a small commission when readers purchase products through our links.